Interactive Demo
What is a network?
A network is a system that connects devices such as computers, smartphones, printers and other electronics allowing them to communicate to sharing information or resources such as files.
Types of network
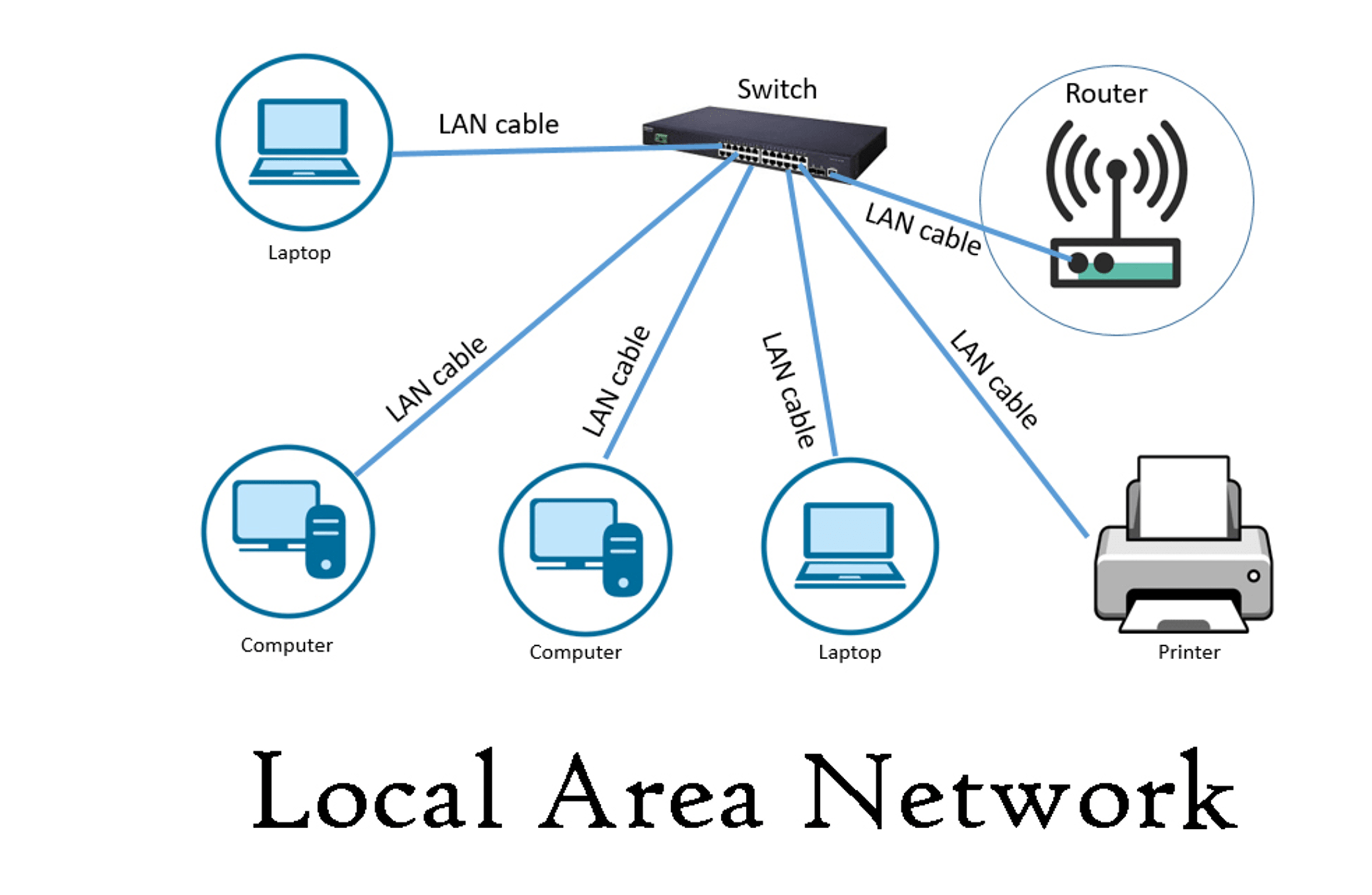
LAN: Local Area Network
A network confined to a small geographic area, like a home, office or school. It allows devices within the area to connect and communicate with each other.
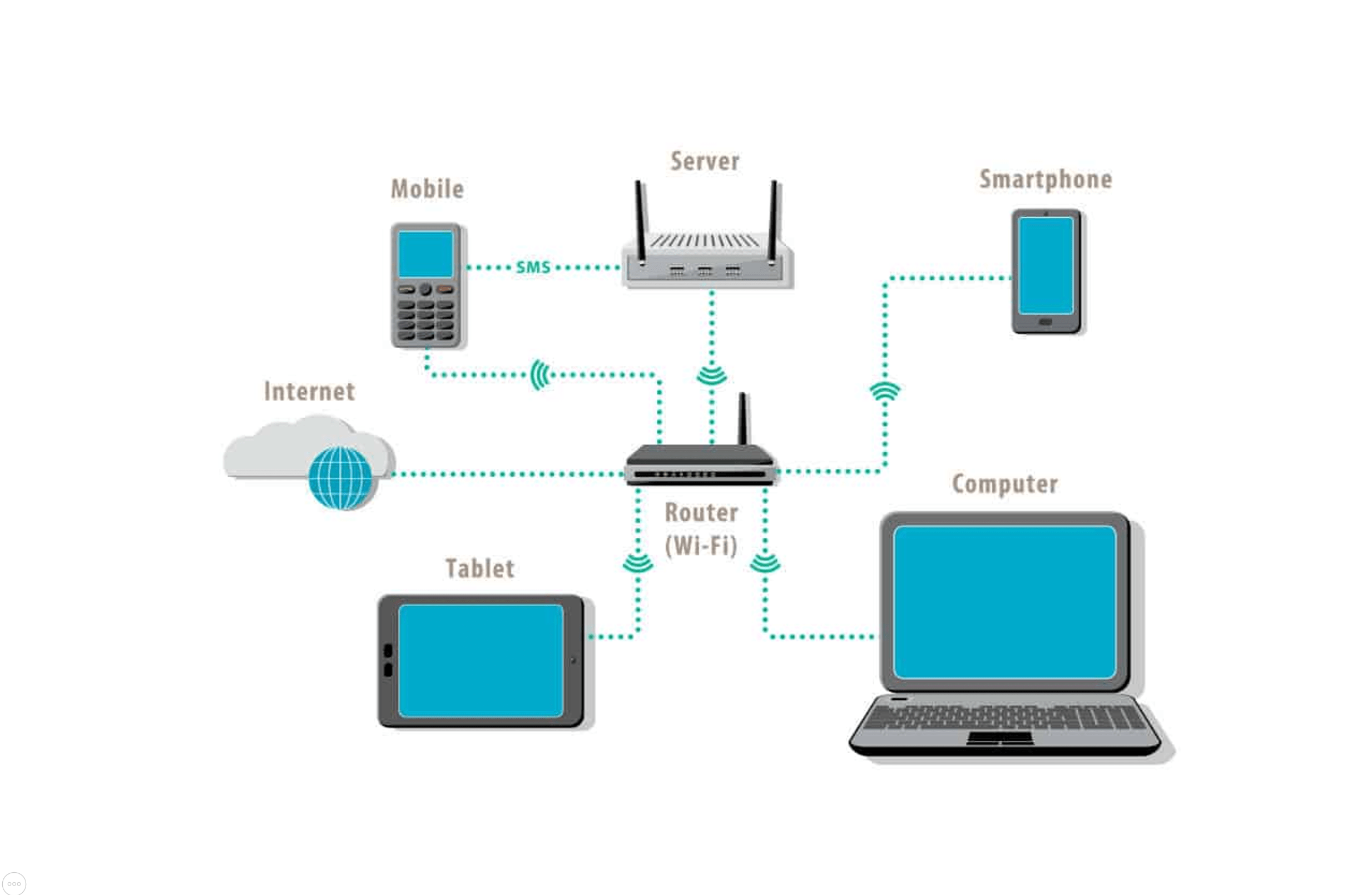
WLAN: Wireless Local Area Network
A type of LAN that uses wireless (Wi-Fi) connections instead of cables to connect devices.
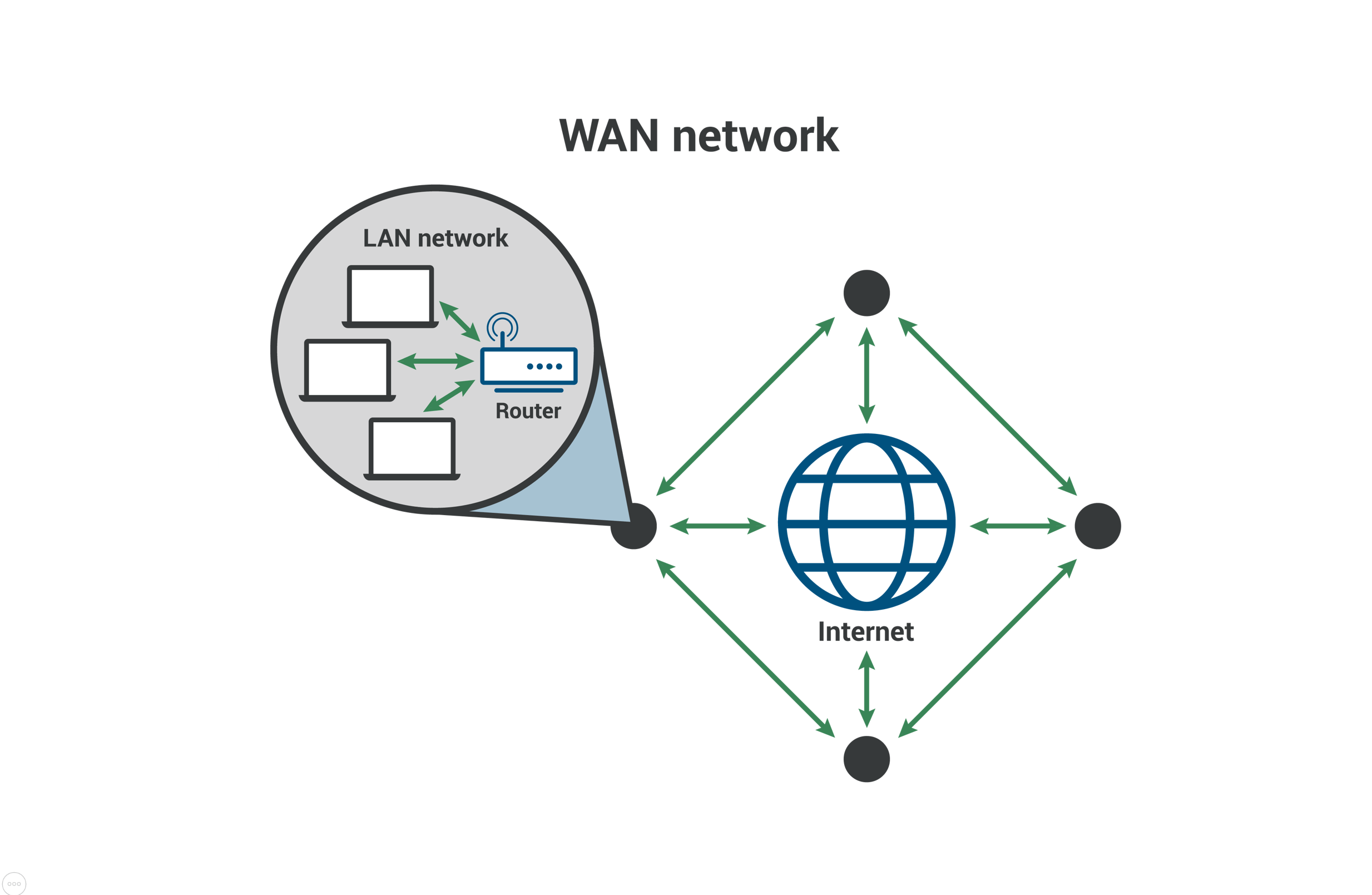
WAN: Wide Area Network
A network that spans a large geographical area, such as a city, country or even globally. The internet is an example of a WAN, connecting multiple LANs together.
IP Address
An IP address (Internet Protocol Adress) is a unique identifier assigned to each device on a network, enabling it to communicate with other devices. There are two ways of obtaining IP Address:
1. Dynamic IP Address (DHCP): Assigned automatically by the router. It can change every time the device reconnects to the network.
2. Static IP Address: Device has manually assigned and does not change, making it suitable for devices that need a fixed address.
Tip: During events is highly recommendable to use static IPs for the important laptops (server, areas, info screens) so we can have full control on the network.
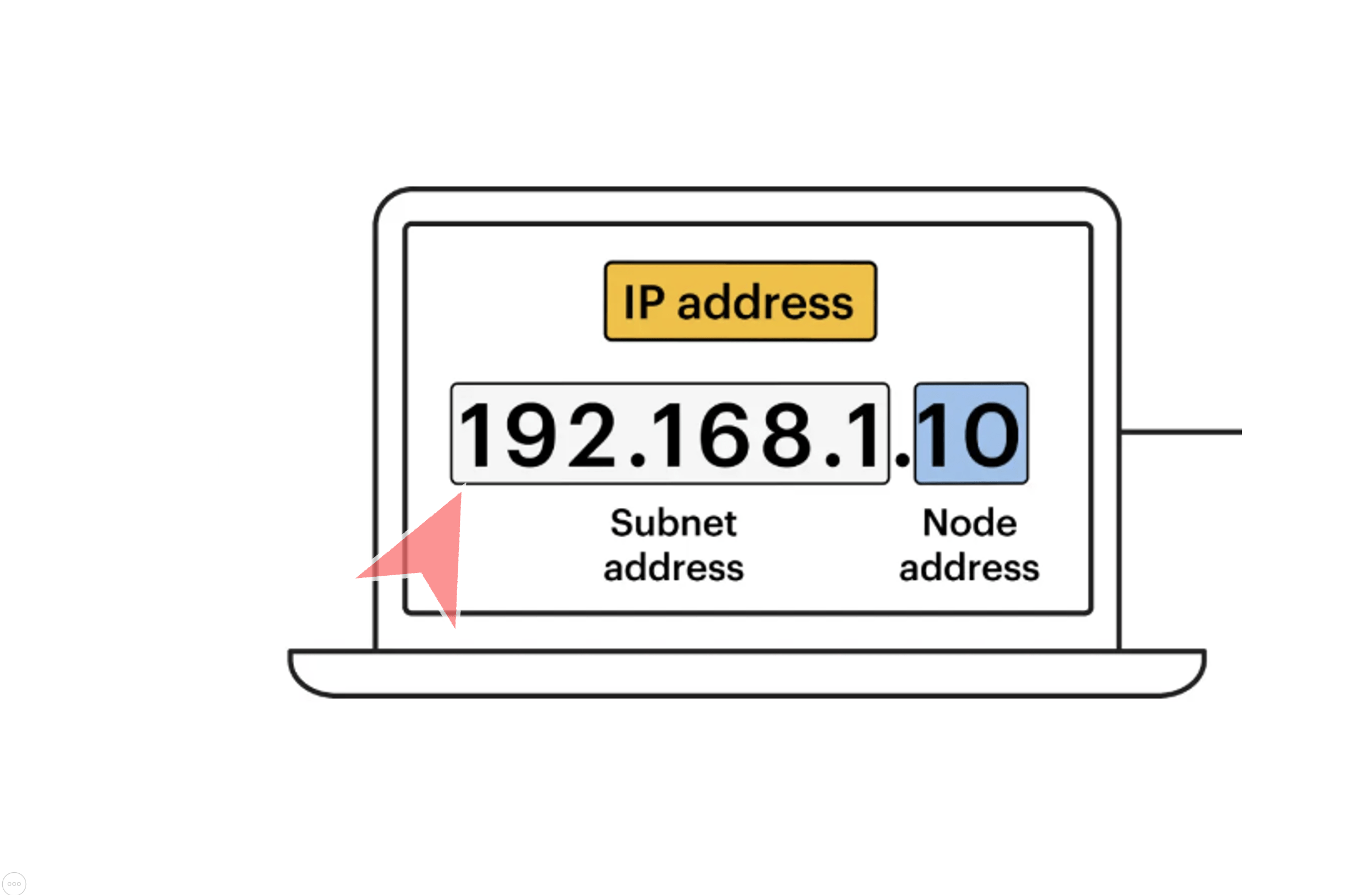
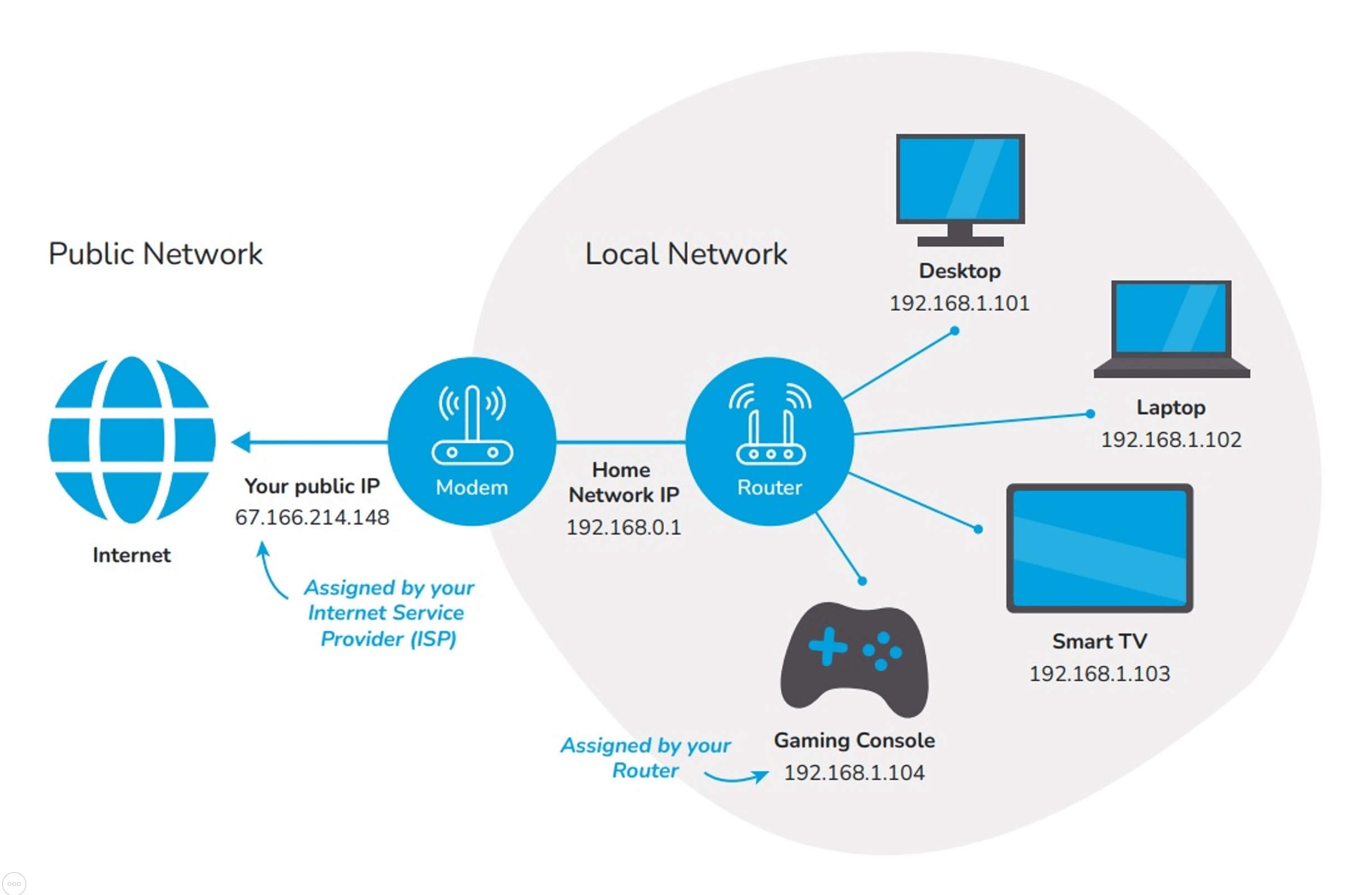
An IP address is made up of four “groups” (technically called octets), separated by dots. Each group is a number between 0 and 255. Generally, the first three groups represent the network address (which is the same for all devices), while the last group is unique to each device.
Example of a LAN connected to internet.
How to setup static IP Address
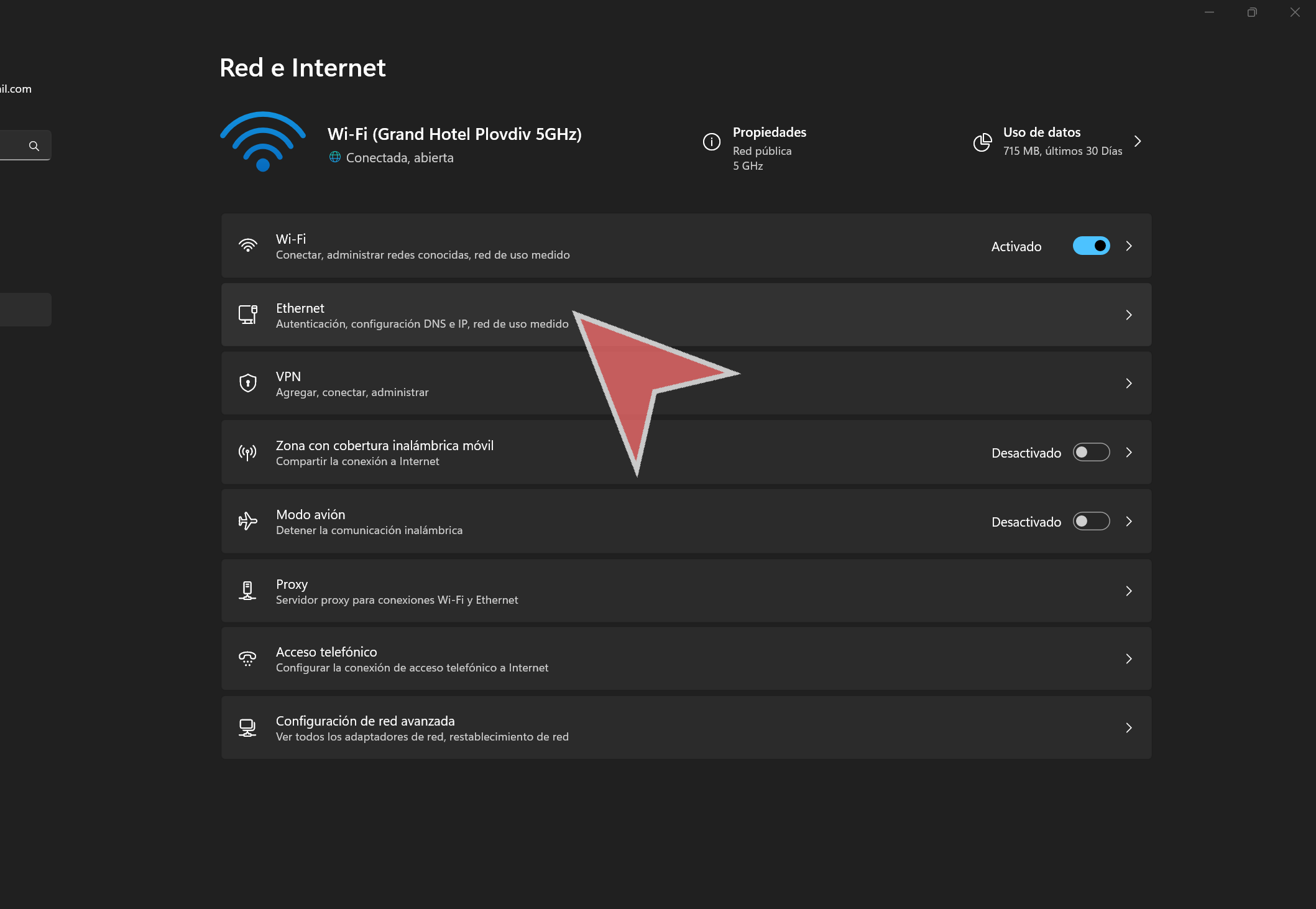
Right-click on the network icon in the system tray (bottom right of the taskbar). Select Network and internet settings.
Click on the “Ethernet” section if you are connected via cable, or on “Wi-Fi” if you wish to set up a static IP for a wireless connection.
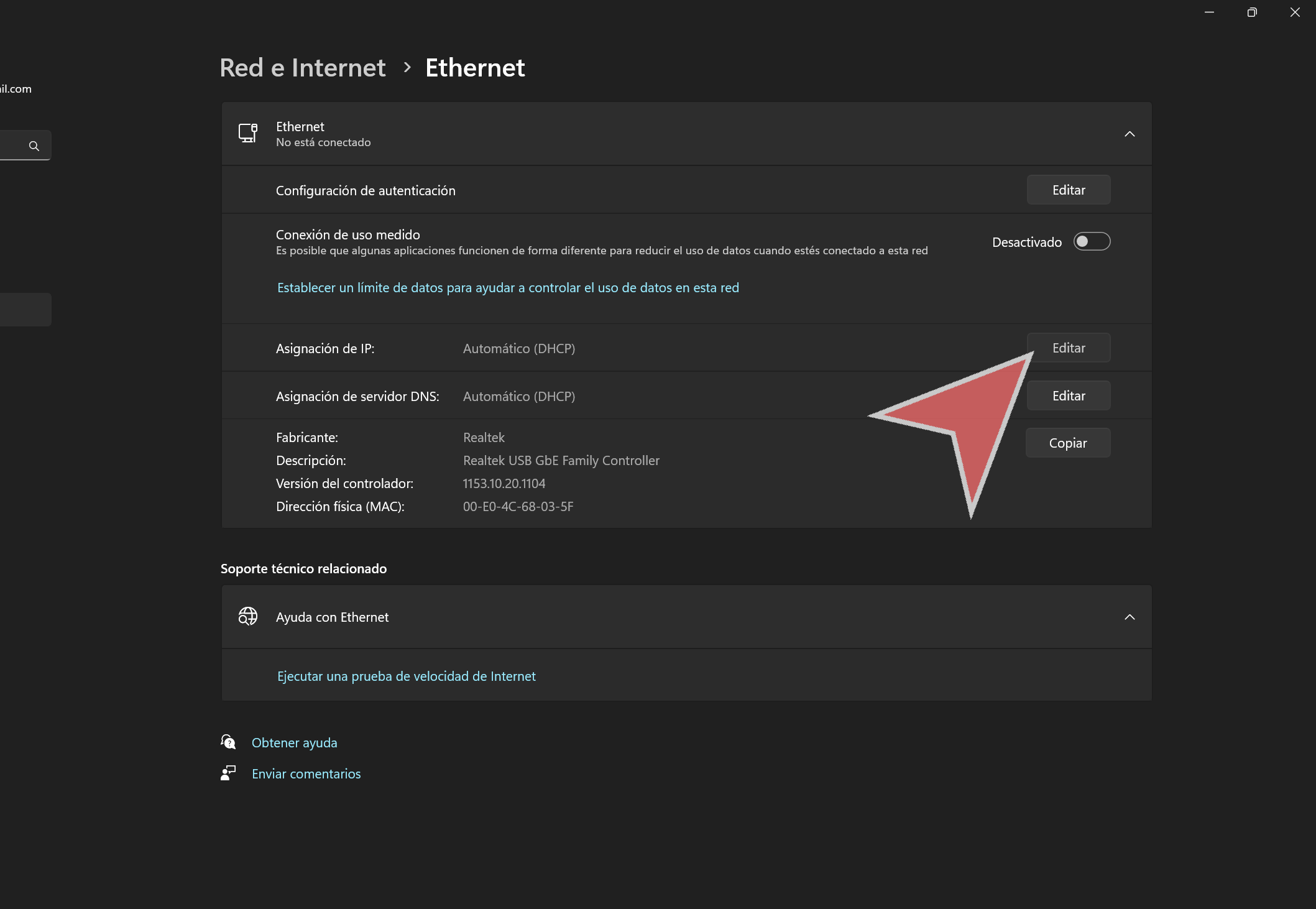
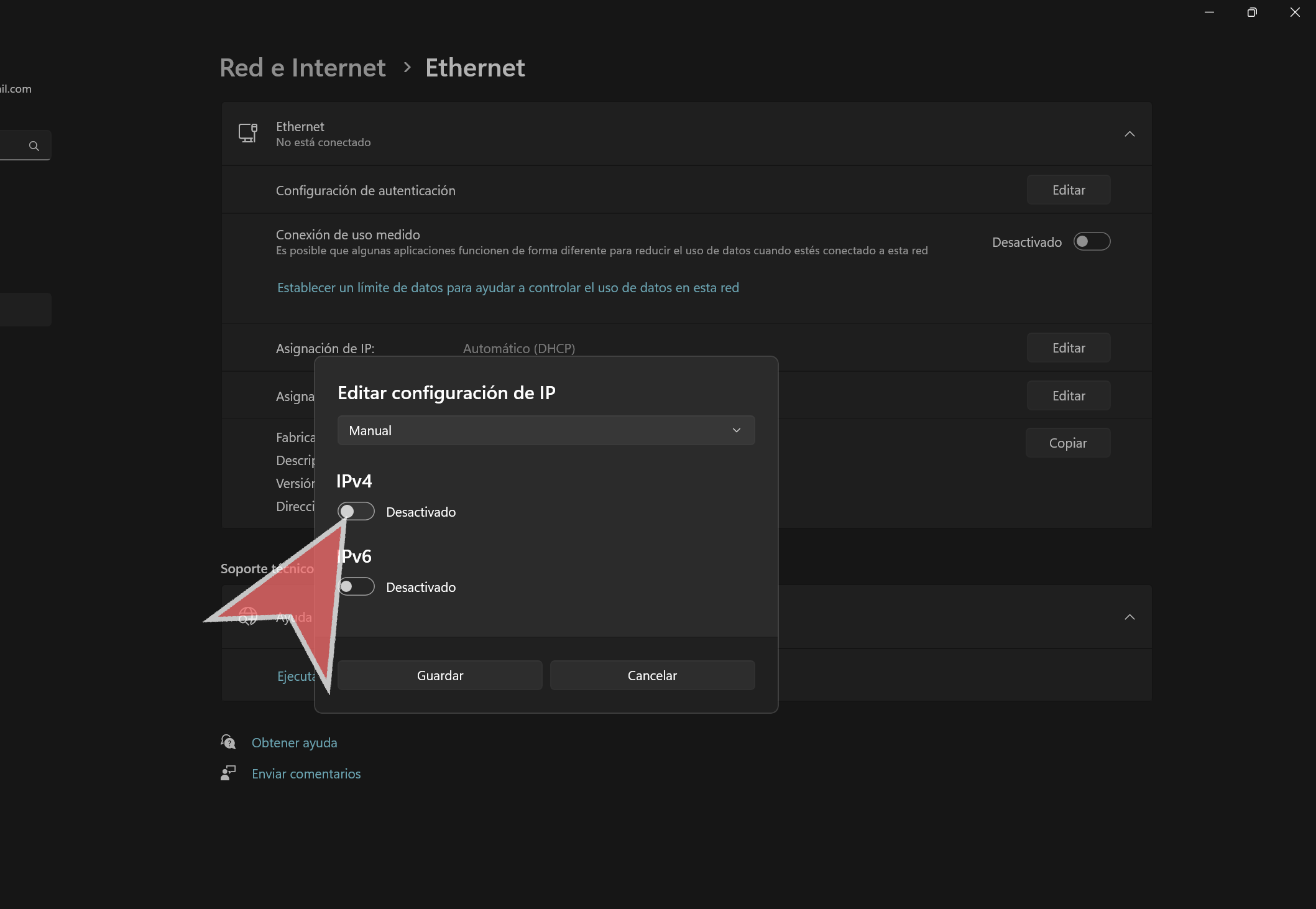
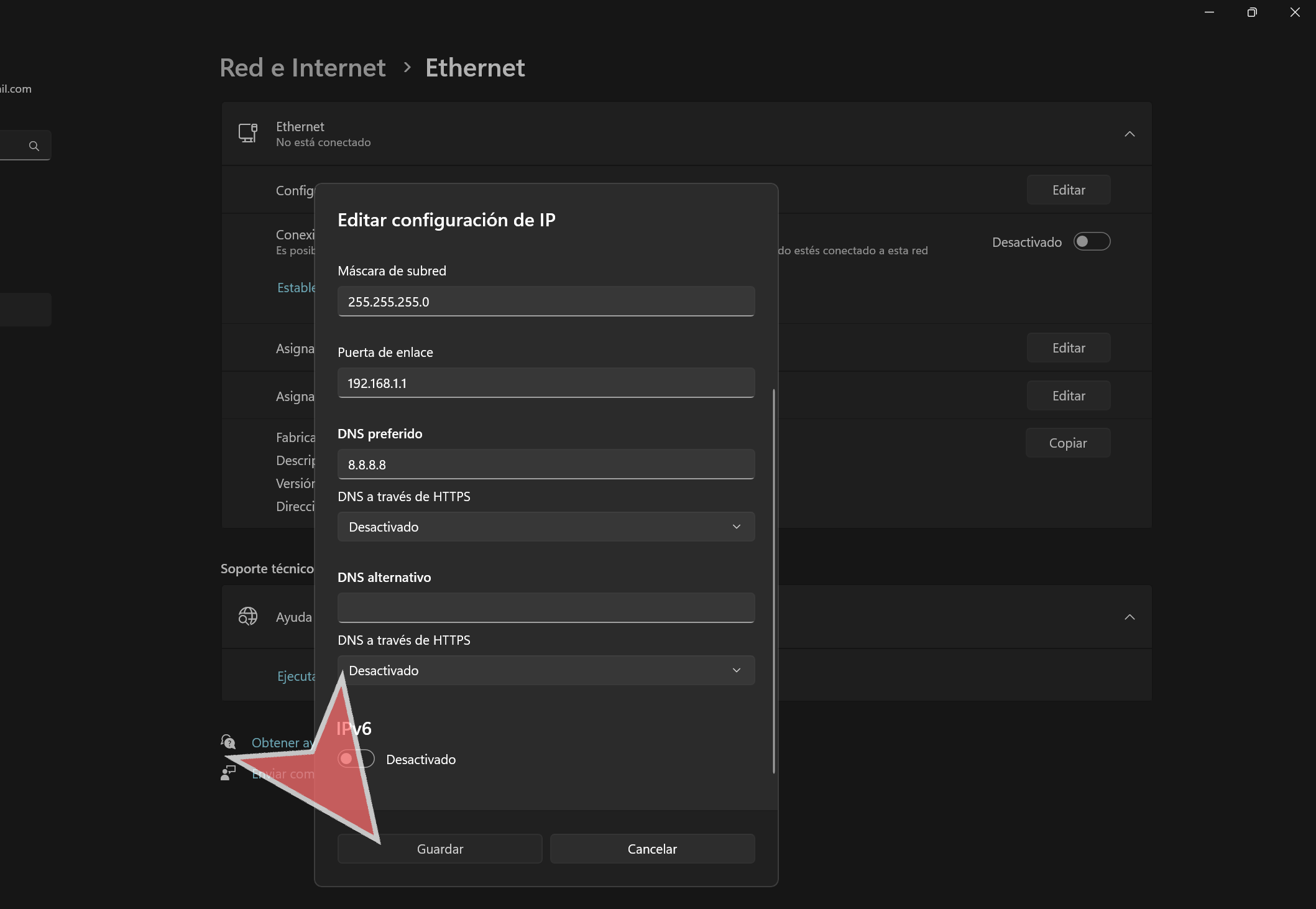
Click on “Edit” in the IP Address assignment section.
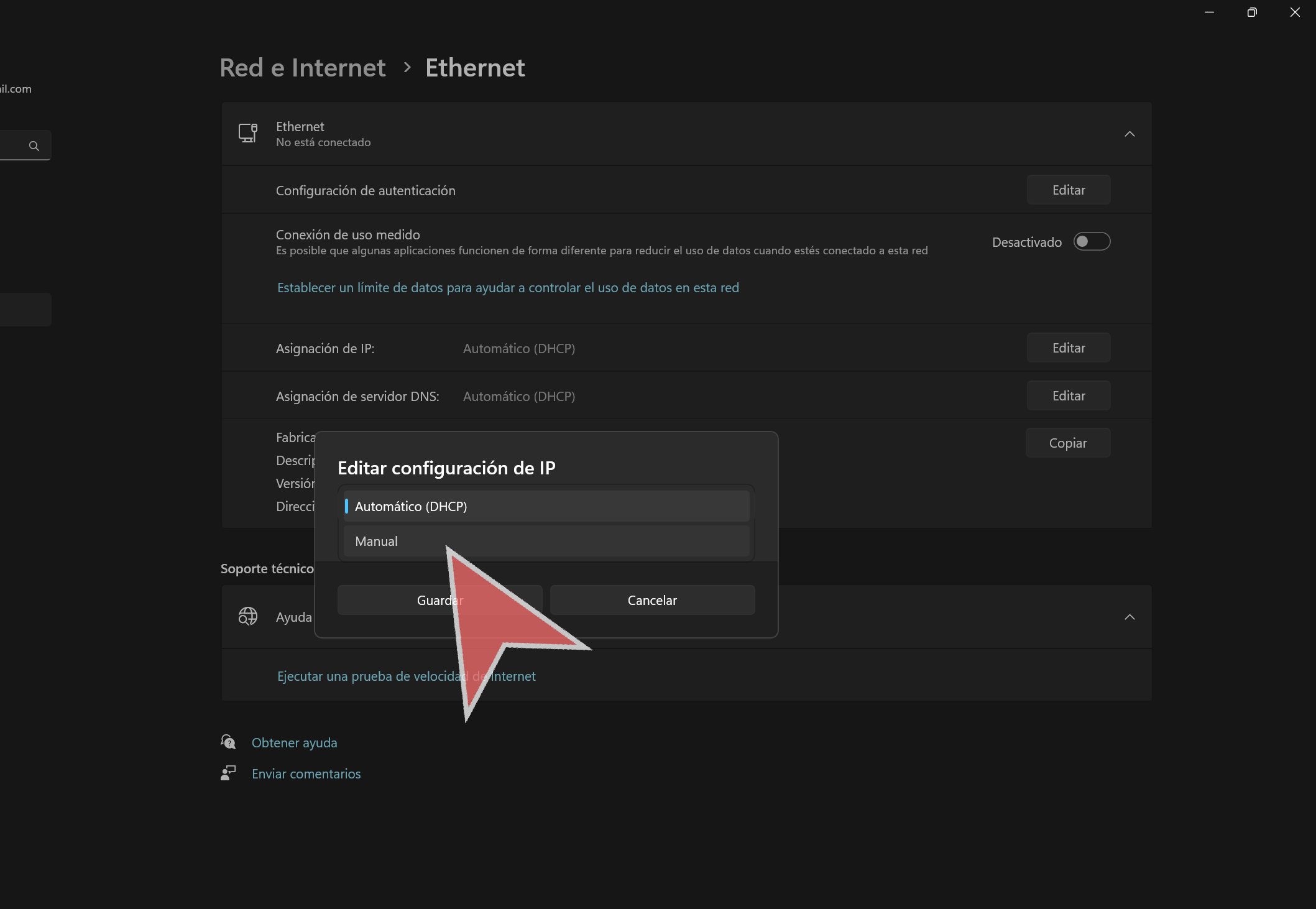
In the dropdown menu, select “Manual”.
Click on the “IPv4” button to access the IP settings.
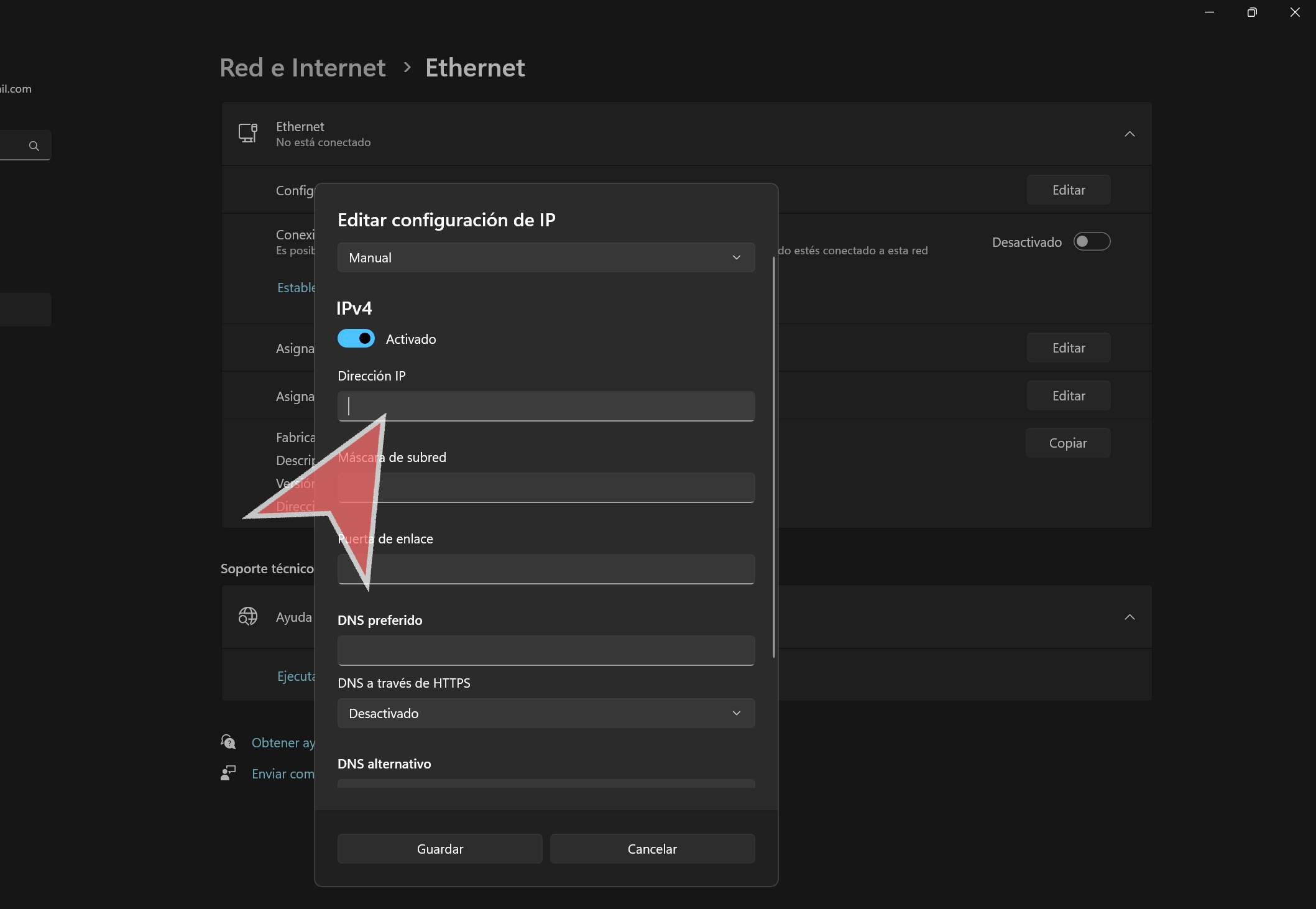
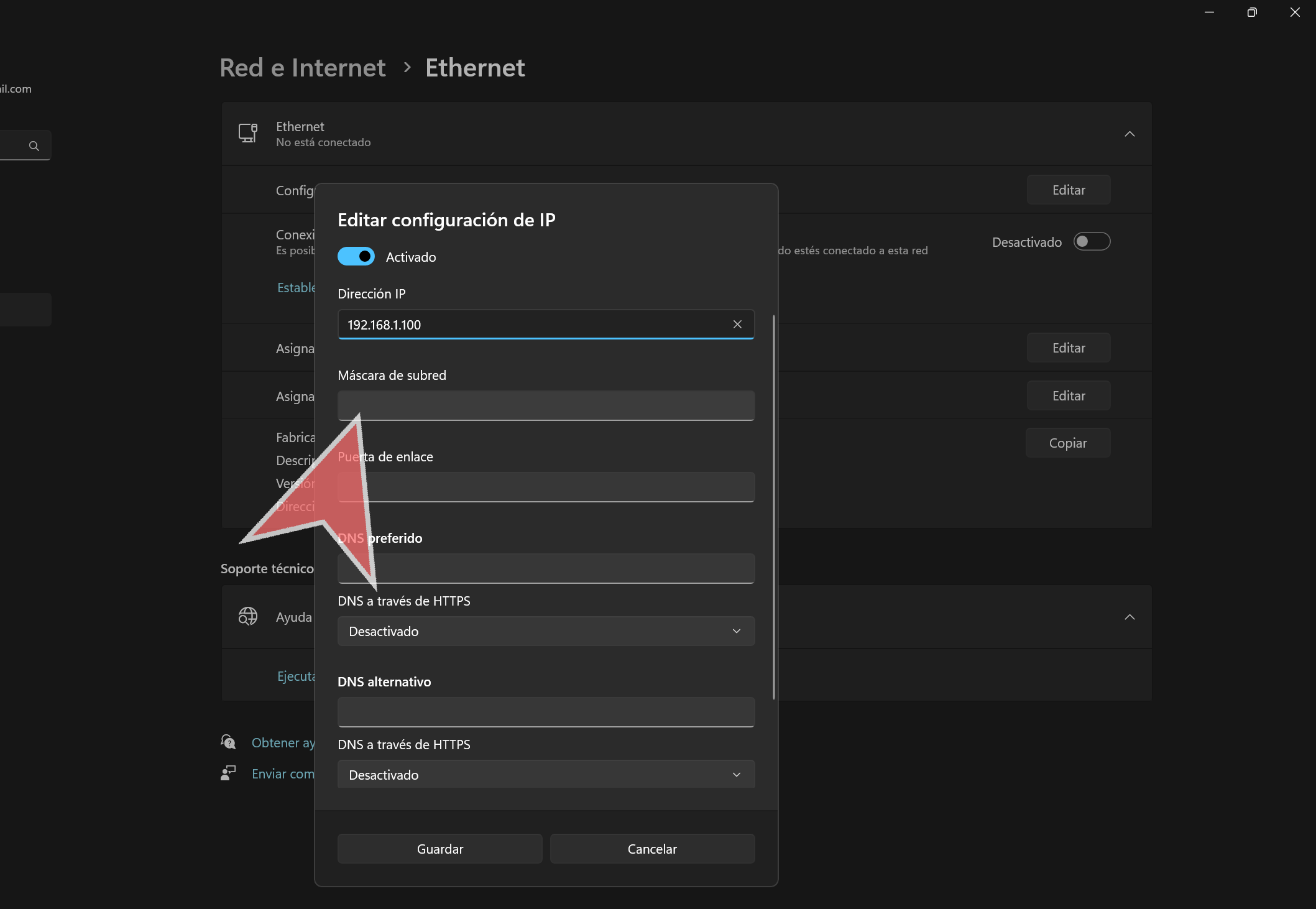
In the “IP Address” field, type the desired IP address.
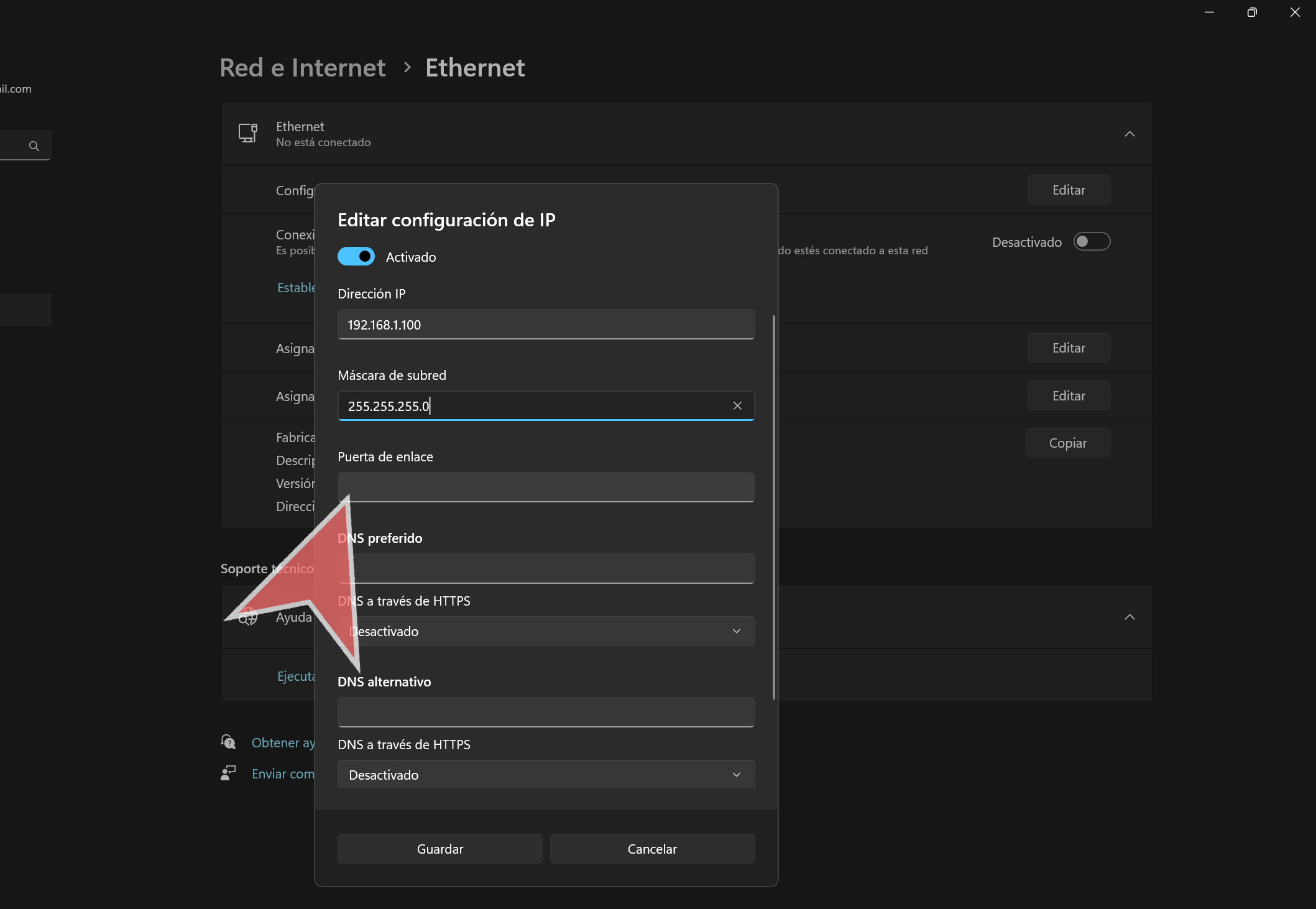
In the “Subnet Mask” field, type “255.255.255.0”.
In the “Gateway” field, type the router’s IP address.
Typically, this is the network address followed by “.1”. For example, it would be “192.168.1.1” for this network.
In the “Primary DNS” field, type “8.8.8.8”.
Click on “Save”.
Test a network – Ping command
The ping command is a network utility used to test the connection between your device and another device. It sends small “packets” of data to the target device and measures how long it takes to receive a response. This helps diagnose network issues and test network configurations.
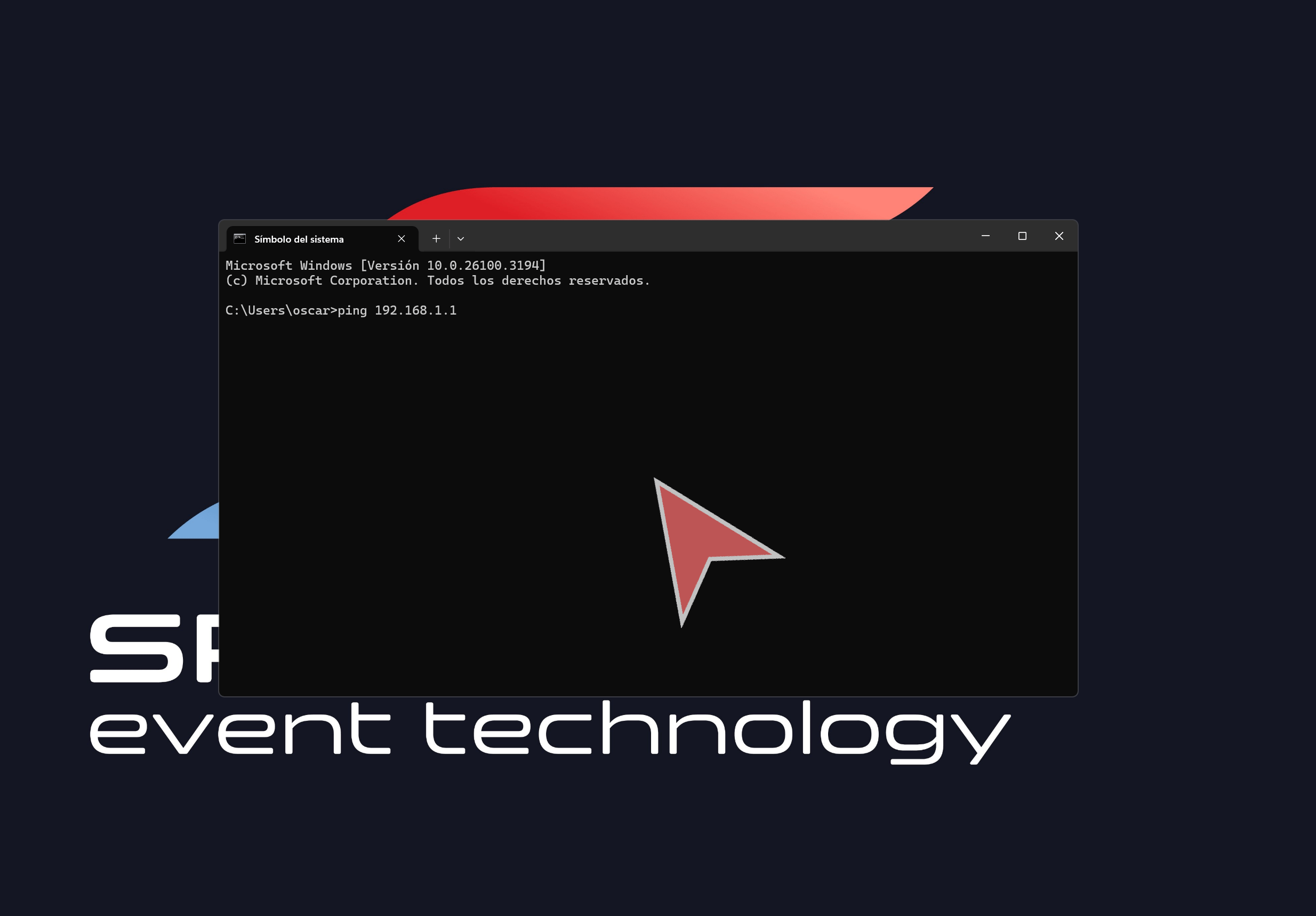
Press the Windows key and type “cmd” to open the Windows Command Prompt.
To use it, type “ping” followed by the IP address you want to test the connection with and hit the Enter key to execute the command.
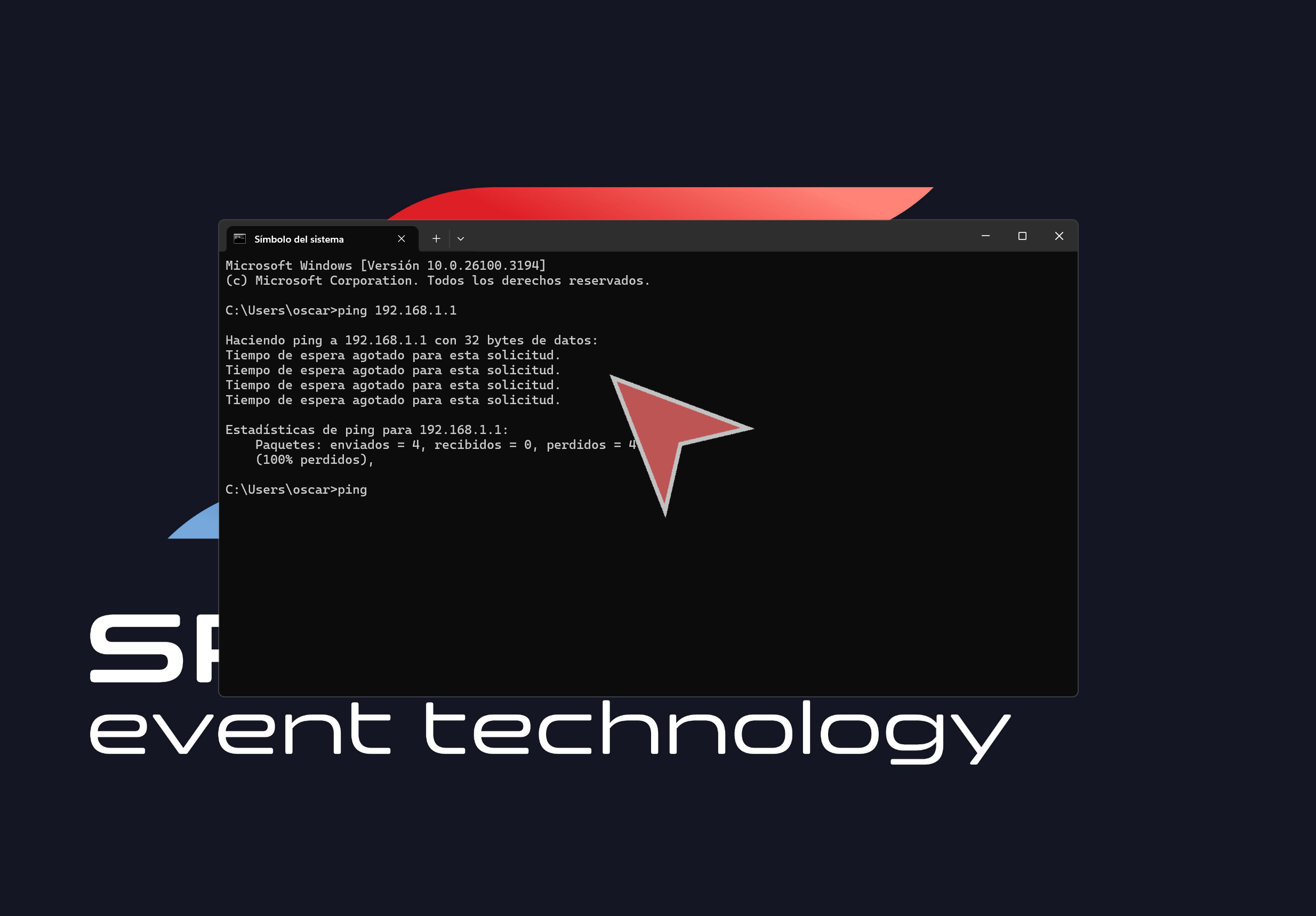
If you see “Response timeout,” “Cannot reach destination address,” or any similar error, it means your device cannot connect to the specified device. This could indicate a network issue or that the target device is offline.
At the end, you will see statistics including the number of packets sent, packets received, packets lost, and the average response time. These details help assess the quality and stability of the connection.
An example of a successful ping command would show a response and response time.
For a wired LAN, the average response time of a healthy network should be 1ms or less.